Our Specializations
Cardiology
End-stage heart failure refers to the most advanced and severe form of heart failure. Heart failure occurs when the heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the body's needs. In end-stage heart failure, the heart's pumping function is significantly impaired, and the condition has progressed to a life-threatening stage.
Some common causes of end-stage heart failure include:
2. Dilated cardiomyopathy: A condition in which the heart chambers become enlarged and weakened, reducing the heart's pumping ability.
...
4. Valvular heart disease: Conditions such as severe aortic stenosis or mitral regurgitation can lead to heart failure if left untreated.
In end-stage heart failure, the symptoms are severe and may include:
1. Shortness of breath, even at rest or with minimal exertion.
2. Fatigue and weakness.
3. Swelling in the legs, ankles, and feet (edema).
4. Rapid or irregular heartbeat.
5. Persistent cough or wheezing.
6. Decreased appetite and nausea.
7. Weight loss.
Treatment options for end-stage heart failure aim to alleviate symptoms, improve quality of life, and potentially prolong survival. These can include:
1. Medications: Various drugs such as diuretics, angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE)
inhibitors, beta-blockers, and aldosterone antagonists may be prescribed to manage
symptoms and improve heart function.
2. Device therapy: Implantable devices like pacemakers, implantable cardioverter-defibrillators
(ICDs), and ventricular assist devices (VADs) can be used to help regulate heart rhythm and
improve pumping function.
3. Heart transplantation: In severe cases where other treatments are ineffective, heart
transplantation may be considered. However, suitable donor hearts are limited, and not all
individuals are eligible candidates.
4. Palliative Care provided by SGP’s PSA provided by SGP’s PSA: For individuals who are not
eligible for transplantation or prefer a non-invasive approach, Palliative Care provided by
SGP’s PSA provided by SGP’s PSA focuses on symptom management, emotional support, and
enhancing quality of life.
It's important for individuals with end-stage heart failure to work closely with their healthcare team to determine the most appropriate treatment plan based on their specific condition and overall health.

Diabetology
Refractory diabetes, also known as treatment-resistant diabetes, is a condition characterized by persistently high blood sugar levels despite aggressive treatment and adherence to recommended therapies. It is considered a challenging form of diabetes to manage effectively.
In refractory diabetes, the body's ability to regulate blood sugar levels becomes significantly impaired, making it difficult to achieve target glucose control. This condition can occur in both type 1 diabetes (where the body does not produce insulin) and type 2 diabetes (where the body either does not produce enough insulin or becomes resistant to its effects).
...There are several factors that can contribute to the development of refractory diabetes, including:
1. Insulin resistance: Insulin resistance occurs when the body's cells do not respond effectively
to insulin, leading to decreased glucose uptake and increased blood sugar levels.
2. Beta-cell dysfunction: Beta cells in the pancreas produce insulin. In refractory diabetes, the
beta cells may not function optimally, resulting in insufficient insulin secretion.
3. Inadequate treatment: In some cases, the treatment approach or medication regimen may
not be adequate to control blood sugar levels. This can occur due to medication non-
compliance, improper dosing, or the need for more intensive therapy.
4. Other health conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as hormonal imbalances, chronic
kidney disease, or liver disease, can complicate diabetes management and contribute to
refractory diabetes.
Managing refractory diabetes requires a comprehensive and individualized approach. Some strategies that may be employed include:
1. Medication adjustments: The healthcare provider may review and modify the dosage or type
of diabetes medications prescribed, such as insulin, oral medications, or injectable incretin-
based therapies, to optimize glucose control.
2. Combination therapy: Combining multiple medications with different mechanisms of action
can help target different aspects of glucose regulation simultaneously.
3. Insulin therapy optimization: Adjusting the insulin regimen by considering factors like timing,
types of insulin, and dosing patterns can improve blood sugar control.
4. Lifestyle modifications: Emphasizing healthy eating habits, regular physical activity, stress
management, and weight management can positively impact blood sugar control.
5. Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM): CGM devices provide real-time glucose readings,
allowing for more frequent monitoring and timely adjustment of treatment strategies.
6. Insulin pump therapy: Insulin pump usage provides more precise and customizable insulin
delivery, potentially enhancing glucose control.
7. Evaluation for underlying conditions: Assessing and managing any underlying medical
conditions that contribute to insulin resistance or impaired glucose regulation is crucial.
8. Collaborative care: Working closely with an endocrinologist or diabetes specialist, diabetes
educators, and other healthcare professionals can provide the necessary expertise and
support for managing refractory diabetes effectively.
Refractory diabetes requires ongoing monitoring, regular follow-up visits, and a multidisciplinary approach to achieve the best possible outcomes. It's essential for individuals with refractory diabetes to remain proactive, engaged, and communicative with their healthcare team to ensure appropriate adjustments to their treatment plan as needed.
arthritis
The department of general Orthopedic has qualified Consultant which carries out treatment of total knee joint replacement, total hip replacements, microdiscectomy, Lumbar spondylitis, cervical spondylitis, Rheumatoid arthritis, joint inflammation cox arthrosis etc.,
The general understanding of the afore mentioned diseases is in the replacement of these joints, the clinicians were able to delay the necessity of an operating procedure without compromising on the quality of life through the concepts based on the Poly Scientific Ayurveda™ methodology where the patients are educated about the disease and the lifestyle modifications to be made for improving the clinical outcomes .
...To meet the ever-growing orthopedic needs of the community, the integrative Orthopedic department of the Hospital has expanded its commitment to patient care, research and education. Is trying to methods of abhyanga, Kati vasthi, Janu vasti, Greevavasti ect other ayurvedic massages should be into main stream orthopedic interventions through Poly Scientific Ayurveda™. Authors of PSA have patent pending technologies for regeneration of various joints.
Neurology
Neurological diseases (Paralysis, Dementia, Alzheimer;s and other conditions)
Paralysis refers to the loss of muscle function in a specific area of the body, resulting in a loss of voluntary movement and control. It can be caused by various factors, including stroke, spinal cord injury, nerve damage, or certain medical conditions.
Stroke, on the other hand, is a medical emergency that occurs when the blood supply to the brain is disrupted, either due to a blockage (ischemic stroke) or bleeding (hemorrhagic stroke). The lack of blood flow deprives brain cells of oxygen and nutrients, leading to their damage or death. Depending on the location and extent of the brain injury, stroke can result in different types and degrees of paralysis.
...Treatment options for paralysis and stroke depend on the underlying cause and specific symptoms. They may include:
1. Medications:
- Clot-busting drugs (thrombolytics): Administered within a specific time window after an ischemic stroke to dissolve blood clots and restore blood flow.
- Anticoagulants or antiplatelet drugs: Prescribed to prevent the formation of blood clots and reduce the risk of stroke recurrence.
- Medications for managing complications: Medications may be given to control high blood pressure, manage pain, prevent seizures, or manage other medical conditions associated with stroke or paralysis.
2. Rehabilitation therapy:
- Physical therapy: Focuses on improving strength, balance, coordination, and mobility through exercises and specialized techniques.
- Occupational therapy: Aims to enhance the ability to perform activities of daily living, such as self-care, using adaptive devices, and modifying the environment.
- Speech therapy: Helps individuals regain communication skills, address swallowing difficulties, and improve speech and language abilities.
- Rehabilitation nursing: Provides specialized nursing care to manage complications, promote recovery, and support functional independence.
3. Assistive devices and mobility aids:
- Mobility aids: Devices such as wheelchairs, walkers, canes, or braces may be recommended to facilitate independent movement.
- Adaptive equipment: Various tools and devices can assist with activities of daily living, including dressing, eating, and personal care.
- Communication aids: Augmentative and alternative communication (AAC) devices can assist individuals with speech difficulties in expressing themselves.
4. Surgery:
- Carotid endarterectomy: A surgical procedure to remove plaque buildup from the carotid arteries, reducing the risk of future strokes.
- Surgical interventions for specific conditions: In some cases, surgery may be performed to address underlying causes of paralysis, such as spinal cord compression or nerve repair.
5. Supportive care:
- Psychological support: Counseling, support groups, and therapy can help individuals cope with the emotional impact of paralysis and stroke.
- Lifestyle modifications: Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and smoking cessation, can reduce the risk factors for stroke and support overall well-being.
- Home modifications: Adapting the living environment to enhance accessibility and safety, such as installing grab bars, ramps, or stairlifts.
The treatment plan for paralysis and stroke is typically individualized and may involve a multidisciplinary team of healthcare professionals, including neurologists, physiatrists, rehabilitation specialists, nurses, and therapists.
It's important to seek immediate medical attention in the case of stroke symptoms, as early intervention can significantly improve outcomes. Rehabilitation and supportive care play a crucial role in maximizing functional independence, promoting recovery, and enhancing the quality of life for individuals with paralysis and stroke.
Oncology
Oncological conditions refer to various types of cancers that arise due to uncontrolled and abnormal growth of cells in the body. The causes and etiology of cancer can vary depending on the specific type, but common risk factors include genetic mutations, exposure to carcinogens (such as tobacco or certain chemicals), family history, and lifestyle factors.
Treatment options for cancer can include:
1. Surgery: Surgical removal of cancerous tumors or affected tissues is often performed, aiming
to eliminate or reduce the tumor burden.
2. Radiation therapy: High-energy radiation is used to target and destroy cancer cells, either
externally (external beam radiation) or internally (brachytherapy).
4. Immunotherapy: Stimulating the body's immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells, either through immune checkpoint inhibitors, cancer vaccines, or adoptive cell therapies.
5. Targeted therapy: Drugs designed to specifically target cancer cells with specific genetic or molecular characteristics, blocking the signaling pathways that promote cancer growth and progression.
6. Hormonal therapy: Used for hormone-dependent cancers, this treatment involves blocking or reducing the effects of hormones that promote cancer growth.
7. Precision medicine: Treatment approaches tailored to an individual's specific genetic profile and the characteristics of their cancer.
Palliative Care provided by SGP’s PSA is an important aspect of cancer management and focuses on improving the quality of life for individuals living with cancer. It involves:
1. Symptom management: Palliative Care provided by SGP’s PSA aims to alleviate symptoms
such as pain, nausea, fatigue, and shortness of breath through medication, physical
interventions, and psychological support.
2. Emotional and psychological support: Counseling, therapy, and support groups help
individuals and their families cope with the emotional and psychological impact of cancer
diagnosis and treatment.
3. End-of-life care: Palliative care provides compassionate support for individuals nearing the
end of life, including pain management, emotional support, and assistance with advance
care planning.
4. Supportive care: Palliative care teams collaborate with healthcare providers to address the
overall well-being of individuals with cancer, ensuring comprehensive support for physical,
emotional, and social needs.
The treatment of oncological conditions is highly individualized, and the specific approach depends on the type and stage of cancer, as well as the overall health and preferences of the individual. It is important for individuals diagnosed with cancer to work closely with a multidisciplinary team of healthcare professionals to develop a comprehensive treatment plan that includes both curative interventions and Palliative Care provided by SGP’s PSA support.

Dermatology
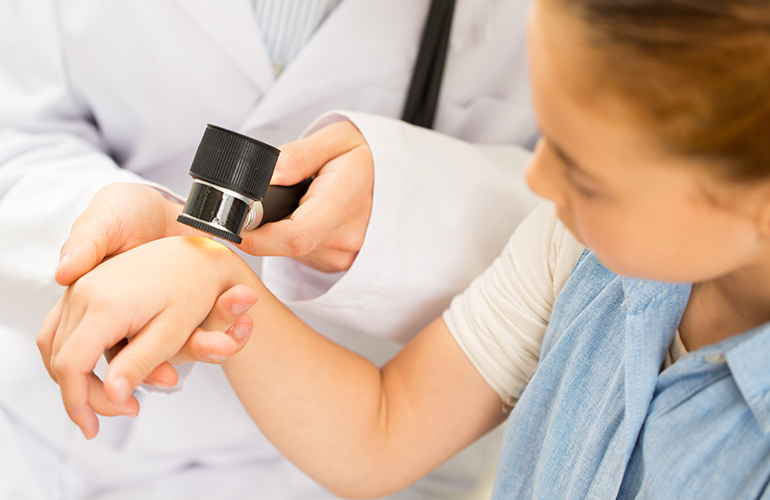

Psoriasis, vitiligo, and other skin diseases are characterized by specific skin abnormalities and can have diverse etiologies and pathogenesis. Treatment options vary depending on the condition, and may include topical medications, systemic therapies, phototherapy, and surgical interventions. Palliative care can provide symptom management, psychological support, and improved quality of life for individuals with chronic skin diseases.
1. Psoriasis:
- Etiology and Pathogenesis: Psoriasis is an autoimmune disease where the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells, resulting in rapid skin cell turnover and the formation of raised, red, and scaly patches.
- Treatment Options: Topical corticosteroids, retinoids, vitamin D analogs, and calcineurin inhibitors are commonly used for mild to moderate psoriasis. Systemic therapies like oral medications (methotrexate, cyclosporine) or biologic agents (TNF inhibitors, interleukin inhibitors) may be prescribed for more severe cases.
2. Vitiligo:
- Etiology and Pathogenesis: Vitiligo is a skin disorder characterized by the loss of melanocytes, resulting in depigmented patches on the skin. The exact cause is unknown, but it is believed to involve autoimmune, genetic, and environmental factors.
- Treatment Options: Treatment for vitiligo aims to halt or slow down depigmentation and may include topical corticosteroids, calcineurin inhibitors, phototherapy (narrowband UVB or excimer laser), or surgical techniques like autologous skin grafting or melanocyte transplantation.
3. Other Skin Diseases:
- Etiology and Pathogenesis: Various skin diseases, such as eczema, acne, rosacea, or dermatitis, have different etiologies and pathogenesis. They can result from factors like genetic predisposition, immune dysfunction, hormonal imbalances, environmental triggers, or infections.
- Treatment Options: Treatment approaches for these skin diseases depend on the specific condition and can include topical medications, oral medications (antibiotics, antihistamines), lifestyle modifications (avoiding triggers, skincare routines), and specific interventions for managing complications or underlying causes.
Palliative care in dermatology aims to improve the overall well-being of individuals with chronic skin diseases through:
- Symptom Management: Providing relief from symptoms such as itching, pain, inflammation, or discomfort through topical treatments, systemic medications, or physical interventions.
- Psychological Support: Addressing the emotional impact of living with a chronic skin disease through counseling, support groups, and strategies to cope with self-esteem or body image issues.
- Education and Self-Care: Empowering individuals with information about their condition, proper skincare routines, and lifestyle modifications to manage their skin disease effectively.
- Quality of Life Enhancement: Promoting strategies to enhance daily functioning, social participation, and overall quality of life for individuals with chronic skin diseases.
It is important for individuals with skin diseases to consult dermatologists or specialists who can provide accurate diagnosis, personalized treatment plans, and appropriate palliative care interventions to address the specific needs of their condition.
Gynecology
Gynecological Diseases
1. Endometriosis:
- Etiology: Endometriosis occurs when tissue similar to the lining of the uterus (endometrium) grows outside the uterus. The exact cause is unknown, but retrograde menstruation, hormonal factors, immune dysfunction, and genetic predisposition are thought to contribute.
- Pathogenesis: Endometrial tissue outside the uterus responds to hormonal changes, causing inflammation, pain, and the formation of adhesions and scar tissue.
- Treatment Options: Treatment includes pain management (NSAIDs), hormonal therapies (birth control pills, progestins, gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists), and surgery (laparoscopy) to remove endometrial implants or adhesions.
2. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS):
- Etiology: PCOS is a hormonal disorder involving imbalances in reproductive hormones, including increased androgen levels. The exact cause is unclear, but insulin resistance, genetic factors, and lifestyle contribute to its development.
- Pathogenesis: PCOS disrupts normal ovarian function, resulting in the formation of cysts, irregular menstrual cycles, and hormonal imbalances.
- Treatment Options: Treatment focuses on managing symptoms and can include lifestyle modifications (diet, exercise, weight loss), medications (oral contraceptives, anti-androgens, metformin), and fertility treatments.
Please note that these summaries provide a simplified overview, and each disease
Palliative care aims to improve the quality of life and provide comprehensive support for individuals with the above-mentioned diseases. Here's a brief overview of palliative care for each disease:
Gastroenterological Diseases:
- Palliative care for gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) focuses on symptom management through medications, dietary modifications, and lifestyle changes. It aims to alleviate symptoms such as heartburn and chest pain, improve nutritional status, and enhance overall well-being.
- For irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), palliative care involves a patient-centered approach that addresses symptom management, psychological support, and education. It focuses on strategies to alleviate abdominal pain, bloating, and bowel habit disturbances, while helping individuals cope with the impact of IBS on their daily lives.
Gynecological Diseases:
- Palliative care for endometriosis aims to provide pain relief through a combination of medications, such as painkillers and hormonal therapies. It also focuses on emotional support, counseling, and education to help individuals manage the emotional and psychological impact of the disease.
- For polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), palliative care may involve lifestyle modifications to address insulin resistance, weight management, and psychological support to manage the emotional aspects of living with PCOS. Fertility counseling and support may also be provided when needed.
It's important to note that palliative care is an integral part of a multidisciplinary approach, working in conjunction with other treatments to optimize symptom management, provide emotional support, enhance communication, and improve the overall well-being of individuals with these diseases. Palliative care teams collaborate with healthcare providers, including gastroenterologists, gynecologists, and other specialists, to develop individualized care plans that address the specific needs and goals of each patient.

Gastroenterology
Gastroenterological and Gynecological Diseases
Gastroenterological Diseases:
1. Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD):
- Etiology: GERD occurs when the lower esophageal sphincter weakens or relaxes inappropriately, allowing stomach acid to flow back into the esophagus. Obesity, hiatal hernia, and certain lifestyle factors contribute to its development.
- Pathogenesis: Chronic acid reflux causes irritation and inflammation of the esophageal lining, leading to symptoms such as heartburn, regurgitation, and chest pain.
- Treatment Options: Lifestyle modifications (dietary changes, weight loss), medications (proton pump inhibitors, H2 blockers), and, in severe cases, surgery (fundoplication) may be recommended to alleviate symptoms and prevent complications.
2. Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS):
- Etiology: The exact cause of IBS is unknown, but factors like abnormal intestinal contractions, visceral hypersensitivity, gut-brain axis dysfunction, and changes in gut microbiota are thought to play a role. Stress, diet, and genetic factors may also contribute.
- Pathogenesis: IBS is a functional disorder characterized by abdominal pain, bloating, and changes in bowel habits without detectable structural abnormalities.
- Treatment Options: Treatment focuses on symptom management and may include dietary modifications, stress reduction techniques, medications (antispasmodics, laxatives), and probiotics.
3. Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD):
- Etiology: Inflammatory bowel disease encompasses Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. The exact cause is unknown, but it involves an abnormal immune response triggered by genetic and environmental factors in individuals with a predisposition.
- Pathogenesis: IBD is characterized by chronic inflammation of the digestive tract. Crohn's disease can affect any part of the gastrointestinal tract, while ulcerative colitis primarily involves the colon.
- Treatment Options: Treatment aims to reduce inflammation, induce remission, and prevent relapses. Medications (aminosalicylates, corticosteroids, immunomodulators, biologic agents), lifestyle changes, nutritional support, and, in severe cases, surgery may be employed.
Allergology and Immunology
Allergies, asthma, and similar diseases involve hypersensitivity reactions of the immune system. They have diverse etiologies and pathogenesis, with treatment options including avoidance of triggers, medications (such as antihistamines and bronchodilators), immunotherapy, and lifestyle modifications. Palliative care provides symptom management, emotional support, and education to improve the quality of life for individuals with these conditions.
...1. Allergies:
- Etiology and Pathogenesis: Allergies result from an exaggerated immune response to normally harmless substances (allergens) like pollen, dust mites, or certain foods. The immune system releases histamine and other chemicals, leading to symptoms such as sneezing, itching, hives, or anaphylaxis.
- Treatment Options: Treatment involves allergen avoidance, medications like antihistamines, nasal corticosteroids, or epinephrine for severe reactions, and allergen immunotherapy (allergy shots) to desensitize the immune system.
2. Asthma:
- Etiology and Pathogenesis: Asthma is a chronic inflammatory condition characterized by airway inflammation and hyperreactivity. Triggers like allergens, irritants, or exercise can lead to airway constriction, coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath.
- Treatment Options: Management includes avoiding triggers, using inhalers (bronchodilators, corticosteroids), leukotriene modifiers, and long-acting beta- agonists. Severe cases may require biologic therapies or oral corticosteroids.
3. Similar Diseases (e.g., allergic rhinitis, atopic dermatitis):
- Etiology and Pathogenesis: These conditions result from immune system dysregulation and can be influenced by genetic factors, environmental exposures, and immune responses to allergens or irritants.
- Treatment Options: Treatment may involve allergen avoidance, medications like antihistamines, nasal corticosteroids, or topical creams, and lifestyle modifications to manage symptoms and prevent flare-ups.
Palliative care for allergies, asthma, and similar diseases focuses on:
- Symptom Management: Providing relief from symptoms such as nasal congestion, itching, wheezing, or skin irritation through medications, environmental control measures, or allergen avoidance.
- Emotional Support: Addressing the psychological impact of living with chronic respiratory or allergic conditions through counseling, education, and support groups.
- Education and Self-Management: Empowering individuals with knowledge about their condition, proper medication use, asthma action plans, and allergen avoidance strategies to better manage their symptoms.
- Quality of Life Enhancement: Promoting strategies to maintain optimal respiratory function, manage triggers, and improve overall well-being for individuals with chronic respiratory or allergic diseases.
Seeking medical advice from allergists, pulmonologists, or specialists in these fields is essential to obtain accurate diagnoses, personalized treatment plans, and appropriate palliative care interventions based on individual needs.
Diagnostics with Docture Poly

The Laboratory service is an important component of any health care center. We all know today investigations play a vital role in the management of any illness. They provide us with clues that help decide on the treatment modality.
The understanding of a disease as such and treatment of the symptoms is the limitation in the modern science. Diagnosis of a disease is the most important part in the treatment, where the modern medicine fails to understand the cause of the diseases and thus failing in the treatment modalities.
At Poly Scientific Ayurveda™ center, the diagnosis is based on the ancient Ayurvedic system of diagnosis (NaadiPareeksha) which helps in understanding the constitutions of the 3 agents called the Vaatha , Pittha and Kapha in each of the 7 tissues and 42 organs.
...